A step forward in the development of in situ product recovery by reactive separation of protocatechuic acid
Abstract
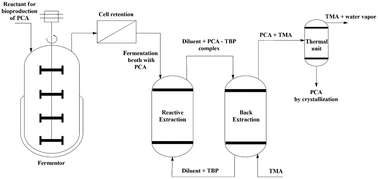
The development of in situ product recovery (ISPR), i.e., integrated bioconversion with a product separation and recovery system, is crucial for a competitive and sustainable technology for biotechnological protocatechuic acid (PCA) production. The major impediment to this development is the toxicity of extractants towards fermenting microorganisms. An initiative for the development of an integrated PCA fermentation–separation system by reactive extraction using tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) in canola oil and groundnut oil was conducted experimentally. The toxic effect of the extractant was circumvented by using non-toxic natural diluents which prevented the contact between the organic phase and organism. The extraction equilibrium complexation constant, dimerization constant, distribution coefficient, partition coefficient, loading ratio, and extraction efficiency were evaluated. The maximum extraction efficiency of 95% for canola oil and 90% for groundnut oil in TBP was achieved in a single cycle. The average distribution coefficient of canola oil (12.14) was higher compared to that of groundnut oil (6.58). Distinctive models represented the equilibrium of PCA using TBP. The findings of this study form the basis for the design of a continuous reactive extraction column and an appropriate ISPR configuration for PCA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...