Insight into the active site nature of zeolite H-BEA for liquid phase etherification of isobutylene with ethanol
Abstract
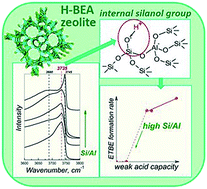
The nature of active acid sites of zeolite H-BEA with different Si/Al ratios (15–407) in liquid phase etherification of isobutylene with ethanol in a continuous flow reactor in the temperature range 80–180 °C has been explored. We describe and discuss data concerning the strength and concentration of acid sites of H-BEA obtained by techniques of stepwise (quasi-equilibrium) thermal desorption of ammonia, X-ray diffraction, low-temperature adsorption of nitrogen, FTIR spectroscopy of adsorbed pyridine and solid-state 27Al MAS NMR. The average values of the adsorption energy of NH3 on H-BEA were experimentally determined as 63.7; 91.3 and 121.9 mmol g−1 (weak, medium, and strong, respectively). In agreement with this, a correlation between the rate of ethyl-tert-butyl ether synthesis and the concentration of weak acid sites (ENH3 = 61.6–68.9 kJ mol−1) has been observed. It was concluded that the active sites of H-BEA for this reaction are Brønsted hydroxyls representing internal silanol groups associated with octahedrally coordinated aluminum in the second coordination sphere.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...