Tailoring intermolecular interactions to develop a low-temperature electrolyte system consisting of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide and organic solvents
Abstract
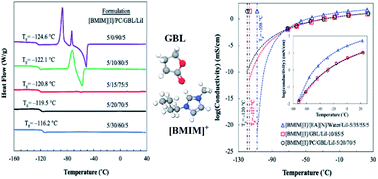
Ionic liquids (ILs) exhibit remarkable properties and great tunability, which make them an attractive class of electrolyte materials for a variety of electrochemical applications. However, despite the promising progress for operating conditions at high temperatures, the development of their low-temperature viability as electrolytes is still limited due to the constrains from thermal and ion transport issues with a drastic decrease in temperature. In this study, we present a liquid electrolyte system based on a mixture of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide ([BMIM][I]), γ-butyrolactone (GBL), propylene carbonate (PC), and lithium iodide (LiI) and utilize its molecular interactions to tailor its properties for extremely low-temperature sensing applications. In particular, the carbonyl group on both PC and GBL can form hydrogen bonds with the imidazolium cation, as indicated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and the extent of these interactions between ions and molecules was also characterized and quantified via proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy. More importantly, at the optimal ratio, the organic solvents do not have excess content to form aggregates, which may cause undesired crystallization before the glass transition. The microscopic evolutions of the systems are correlated with their bulk behaviors, leading to improvements in their thermal and transport properties. The optimized formulation of [BMIM][I]/PC/GBL/LiI showed a low glass transition temperature (Tg) of −120 °C and an effectively reduced viscosity of 0.31 Pa s at −75 °C. The electrochemical stability of the electrolyte was also validated to support the targeted iodide/triiodide redox reactions without interference.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...