Three chiral one-dimensional lanthanide–ditoluoyl-tartrate bifunctional polymers exhibiting luminescence and magnetic behaviors†
Abstract
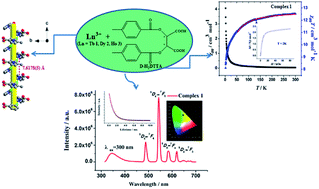
Since Ln-CPs have excellent optical properties (higher color purity, longer fluorescence lifetime and higher quantum yield) and magnetic properties, it is of great significance to prepare dual magneto-optical materials based on Ln(III). Herein, we obtained three versatile Ln-CPs, [Ln(HDTTA)3(CH3OH)3]n, derived from reactions of lanthanide salts (Ln = Tb 1, Dy 2, Ho 3) and a chiral and flexible ligand, namely, (+)-di-p-toluoyl-D-tartaric acid (d-H2DTTA) in a methanol–water solution, at room temperature and pressure. The structures of these compounds have been characterized by single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction, infrared spectroscopy, elemental analyses and thermogravimetric analyses. Complexes 1–3 are isomorphic, crystallizing in the chiral trigonal R3 space group with the linkage of Ln3+ ions and featuring 1D propeller chain structures. The circular dichroism spectra confirm that the complexes maintain the chirality from the ligands. Furthermore, the luminescent and magnetic properties have been investigated, relying on intrinsic properties of the lanthanide ions. The photoluminescence measurements indicate that 1, 2 and 3 show strong green, white and blue emission bands with CIE chromaticity coordinates of (0.32, 0.56), (0.29, 0.26) and (0.21, 0.12), respectively. The decay lifetime curve of 1 shows the exponential decay with long lifetime of 1.169 ms and the relative quantum yield for 1 was 19.31%. In addition, the magnetic properties of complexes 1–3 have been investigated by measuring the magnetic susceptibility in the temperature range of 2–300 K. They are all dominated by spin–orbit coupling and ligand field perturbation, and the exchange coupling between Ln3+ ions is almost negligible. Therefore, complexes 1–3 are promising chiral, optical and magnetic multifunctional materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...