Trichoderma asperellum T42 induces local defense against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae under nitrate and ammonium nutrients in tobacco†
Abstract
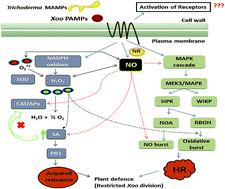
Trichoderma has been explored and found to play a vital role in the defense mechanism of plants. However, its effects on host disease management in the presence of N nutrients remains elusive. The present study aimed to assess the latent effects of Trichoderma asperellum T42 on oxidative burst-mediated defense mechanisms against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) in tobacco plants fed 10 mM NO3− and 3 mM NH4+ nutrients. The nitrate-fed tobacco plants displayed an increased HR when Xoo infected, which was enhanced in the Trichoderma-treated plants. This mechanism was enhanced by the involvement of Trichoderma, which elicited NO production and enhanced the expression pattern of NO-modulating genes (NR, NOA and ARC). The real-time NO fluorescence intensity was alleviated in the NH4+-fed tobacco plants compared to that fed NO3− nutrient, suggesting the significant role of Trichoderma-elicited NO. The nitrite content and NR activity demonstration further confirmed that nitrate metabolism led to NO generation. The production of ROS (H2O2) in the plant leaves well-corroborated that the disease resistance was mediated through the oxidative burst mechanism. Nitrate application resulted in greater ROS production compared to NH4+ nutrient after Xoo infection at 12 h post-infection (hpi). Additionally, the mechanism of enhanced plant defense under NO3− and NH4+ nutrients mediated by Trichoderma involved NO, ROS production and induction of PR1a MEK3 and antioxidant enzyme transcription level. Moreover, the use of sodium nitroprusside (100 μM) with Xoo suspension in the leaves matched the disease resistance mediated via NO burst. Altogether, this study provides novel insights into the fundamental mechanism behind the role of Trichoderma in the activation of plant defense against non-host pathogens under N nutrients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...