Effect of ZnO on (ferroelectric) fatigue retention and thermal stability of ferroelectric properties in lead free (K0.5Na0.5)(Nb0.7Ta0.3)O3 ceramics†
Abstract
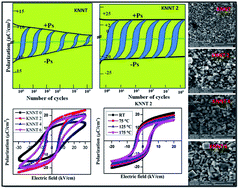
This work investigates and reports the effect of ZnO addition on the ferroelectric properties of (K0.5Na0.5)(Nb0.7Ta0.3)O3 (KNNT) ceramics prepared by a solid state reaction method. Though literature is abundant on the study of the effect of ZnO on the sinterability, microstructure and electrical properties of KNN based materials, the effect of ZnO on their ferroelectric properties has seldom been studied in detail, especially in KNNT. In the current study, 2, 4 and 6 wt% of ZnO was added to KNNT ceramics. The XRD results revealed ZnO addition has no effect on the crystal symmetry of KNNT. However, a ZnO secondary phase was found in KNNT ceramics with 4 and 6 wt% ZnO doping. An increase in grain size was observed with increases in the concentration of ZnO, indicating a direct dependence of grain size on the concentration of ZnO in the KNNT matrix. From ferroelectric studies it was observed that a lower electric field was sufficient to get maximum polarization for ZnO doped KNNT samples compared to that of pure KNNT ceramics. A high remnant polarization (Pr = 14.0 μC cm−2) and lower coercive field (Ec = 5.6 kV cm−1) was obtained for 2 wt% ZnO doped KNNT. These samples showed the least fatigue (0.8%) after 109 cycles in comparison to pure (5%), 4 wt% ZnO doped (24.9%) and 6 wt% ZnO doped (30%) KNNT ceramics. The diminution in Ps, Pr, and Ec was only 26.0%, 26.2% and 18.5%, respectively, with an increase in measurement temperature, which indicates improved thermal stability in 2 wt% ZnO doped KNNT. From the present study the optimum concentration of ZnO in KNNT is identify to be 2.0 wt% and their improved properties in comparison to the pure KNNT ceramics are discussed in detail.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' Collection: Ferroelectric and Multiferroic Materials


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...