Unwanted hydrolysis or α/β-peptide bond formation: how long should the rate-limiting coupling step take?†
Abstract
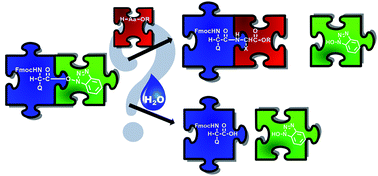
Nowadays, in Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS), being either manual, automated, continuous flow or microwave-assisted, the reaction with various coupling reagents takes place via in situ active ester formation. In this study, the formation and stability of these key active esters were investigated with time-resolved 1H NMR by using the common PyBOP/DIEA and HOBt/DIC coupling reagents for both α- and β-amino acids. Parallel to the amide bond formation, the hydrolysis of the α/β-active esters, a side reaction that is a considerable efficacy limiting factor, was studied. Based on the chemical nature/constitution of the active esters, three amino acid categories were determined: (i) the rapidly hydrolyzing ones (t < 6 h) with smaller (Ala) or even longer side chains (Arg) holding a large protecting group; (ii) branched amino acids (Ile, Thr) with slowly hydrolyzing (6 < t < 24 h) propensities, and (iii) non-hydrolyzing ones, such as the hard-to-couple β-amino acids or β-sugar amino acid derivatives, stable for longer times (t > 24 h) in solution. The current insight into the kinetics of this key hydrolysis side reaction serves as a guide to optimize the coupling conditions of α- and β-amino acids, thereby saving time and minimizing the amounts of reagents and amino acids to be used – all key factors of more environmentally friendly chemistry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...