Influence of serum concentration and surface functionalization on the protein adsorption to mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
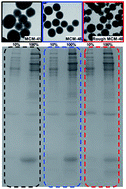
A study of a protein corona on mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) at in vitro and in vivo relevant serum concentrations is presented. Three MSNs different in terms of mesoscopic pore arrangement, surface chemistry, and surface roughness were studied. After incubation in either 10% or 100% serum, the hard protein corona–particle complexes were collected and analyzed by DLS, zeta-potential, and TGA, and the corona proteins were analyzed with SDS-PAGE. A good correlation between SDS-PAGE and TG results in terms of total amounts of proteins adsorbed was established. The results demonstrated that more proteins, especially apolipoproteins, were associated with the particles at higher serum concentration regardless of surface chemistry and morphological differences. Also, the mean molecular weight of the adsorbed proteins was clearly lower under full serum conditions modeling in vivo conditions as compared to under dilute conditions modeling in vitro conditions, but functionalization of the MSNs by carboxylic acid functionalities reduced protein adsorption. The influence of the structural characteristics of the MSNs on the protein adsorption was minor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...