Effects of Bailing capsule on diabetic nephropathy based on UPLC-MS urine metabolomics
Abstract
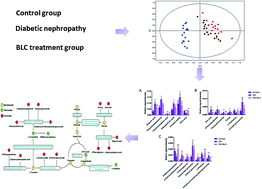
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the most common microvascular diabetes complications and has become a threat to human health. Bailing capsules (BLCs), containing fermentation products of Cordyceps sinensis, have been commonly used for treatment of renal dysfunction, such as DN. However, mechanisms underlying the protective effects of BLC remain largely obscure and await more investigation. In this study, UPLC-MS-based comprehensive metabolomics along with pattern recognition was applied to explore the urine metabolic alteration of DN as well as therapeutic mechanisms of BLC. Nineteen differentially expressed endogenous metabolites were identified related to DN, which were involved in the perturbations of tyrosine metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, glycine metabolism, purine metabolism, glutamine metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, histidine metabolism and TCA cycle metabolism pathways. After drug intervention, most of the biomarkers exhibited a certain extent towards normal levels (P < 0.05), which indicated that BLC was an effective drug for treating DN and might play its therapeutic role by retrieving abnormal metabolism pathways. The data obtained in this research may pave the way for further exploration of DN and provide key clues to understand the protective effect of BLC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...