Photocatalytic primary alcohol oxidation on WO3 nanoplatelets†
Abstract
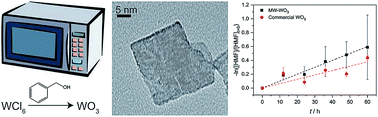
With the aid of direct heating through microwave irradiation in non-aqueous media, nanocrystalline tungsten(VI) oxide is achievable in 30 minutes at 200 °C, faster and at a lower temperature than conventional synthesis methods. Forming in a platelet morphology, these particles are as small as 20 nm with a BET surface area of 37 m2 g−1 WO3. These nanoplatelets are active for the photocatalytic oxidation of the 1° alcohols benzyl alcohol (rate constant, k of 2.6 × 10−3 h−1) and 5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furfural (k of 0.01 h−1) using 10 mg of WO3 with 2 mL of 0.250 M substrate in acetonitrile and a 150 mW cm−2 460 nm blue LED source. As expected, these rate constants are larger than those observed for commercially prepared, micron-sized WO3. XPS analysis shows that during catalysis, the concentration of W5+ on the surface increases, but the nanoplatelets are stable under these reaction conditions. The overall morphology and size of the particles are retained through the reactions. Moreover, the nanoplatelets are recyclable—showing no loss in activity for four reaction cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...