Synthesis and electrochemical performance of NaV3O8 nanobelts for Li/Na-ion batteries and aqueous zinc-ion batteries
Abstract
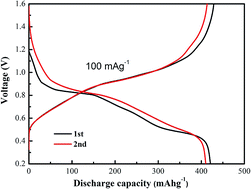
NaV3O8 nanobelts were successfully synthesized for Li/Na-ion batteries and rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) by a facile hydrothermal reaction and subsequent thermal transformation. Compared to the electrochemical performance of LIBs and NIBs, NaV3O8 nanobelt cathode materials in ZIBs have shown excellent electrochemical performance, including high specific capacity of 421 mA h g−1 at 100 mA g−1 and good cycle stability with a capacity retention of 94% over 500 cycles at 5 A g−1. The good diffusion coefficients and high surface capacity of NaV3O8 nanobelts in ZIBs were in favor of fast Zn2+ intercalation and long-term cycle stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...