B-site modified photoferroic Cr3+-doped barium titanate nanoparticles: microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis, photocatalytic and electrochemical properties†
Abstract
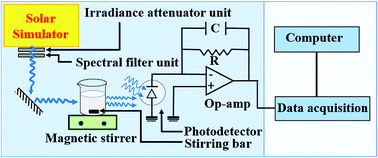
We report on the synthesis of photoferroic Cr3+-doped BaTiO3 nanoparticles with nominal Cr content ranging from 2–8 mol% by a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. The absorption properties of the doped systems are significantly enhanced due to the d–d band transition of Cr3+/4+. The structural properties of the materials are examined on the basis of lattice distortions given by the tolerance factor and microstrain. Raman scattering provides complementary information on the lattice vibrations indicating a softening of the longitudinal optic (LO) phonon mode located at 716 cm−1 with increasing Cr concentration. The charge transport properties investigated through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) demonstrate that there is a reduction in the charge transfer resistance from 5.2 Ω to 4.3 Ω for the undoped and 4 mol% Cr3+-doped respectively, which favors the degradation kinetics. The photo-oxidation ability of the systems is evaluated by time evolution of photodegradation of methyl orange under standardized solar irradiation. The experimental results confirm that the best photocatalytic performance is achieved with the 4 mol% Cr3+-doped BaTiO3 nanoparticles, which is ∼2.7 times higher than for the undoped sample. Evidence of superoxide radical being the dominant active species is provided by in situ reactive oxide species (ROS) capture experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...