Efficient detoxification of triclosan by a S–Ag/TiO2@g-C3N4 hybrid photocatalyst: process optimization and bio-toxicity assessment †
Abstract
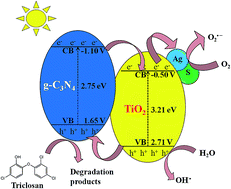
Owing to their persistency and toxicity, development of an effective strategy to eliminate antibiotic residues from the aquatic system has become a major environmental concern. Doping TiO2 with hetero atoms and forming a hybrid structure with g-C3N4 could serve as an efficient visible light active photocatalytic candidate. In this study, a novel S–Ag/TiO2@g-C3N4 hybrid catalyst was prepared for visible light degradation and detoxification of triclosan (TS) antibiotic. The effect of various operational parameters towards the photocatalytic degradation was systematically evaluated through response surface methodology (RSM) based on central composite design (CCD). The highest TS degradation (92.3%) was observed under optimal conditions (TS concentration = 10 mg L−1, pH = 7.8, and catalyst weight = 0.20 g L−1) after 60 min. Efficient charge separation resulted from the doped nanoparticles (silver and sulphur), the existing integrated electric field of the heterojunction and the overlying light response of hybridized TiO2 and g-C3N4, thus the S–Ag/TiO2@g-C3N4 composite showed impressively higher activity. The main degradation products of TS were identified by LC/ESI-MS analysis. In addition, the toxicity of the degradation products was investigated through an Escherichia coli (E. coli) colony forming unit assay and the results revealed that under optimal conditions a significant reduction in biotoxicity was noticed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' Collection: Nanomaterials for the environment


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...