The relationship between crystalline disorder and electronic structure of Pd nanoparticles and their hydrogen storage properties†
Abstract
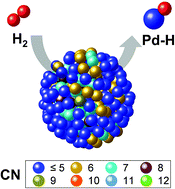
We investigated the relationship between crystalline disorder and electronic structure deviations of Pd nanoparticles (NPs) and their hydrogen storage properties as a function of their particle diameter (2.0, 4.6 and 7.6 nm) using various synchrotron techniques. The lattice constant of the 2.0 nm-diameter Pd NPs was observed to be larger than that of the 4.6 or 7.6 nm-diameter Pd NPs. With increasing particle diameter the structural ordering was improved, the lattice constant and atomic displacement were reduced and the coordination numbers increased, as determined using high-energy X-ray diffraction, reverse Monte Carlo modelling and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The structural order of the core part of the larger NPs was also better than that of the smaller NPs. In addition, the bond strength of the Pd–H formation increased with increasing particle diameter. Finally, the surface order of the Pd NPs was related to enhancement of the hydrogen storage capacity and Pd–H bond strength.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...