A graphite-modified natural stibnite mineral as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion storage
Abstract
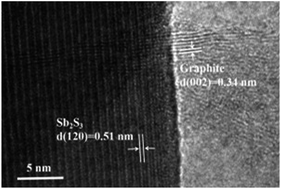
Recently, Sb2S3 has drawn extensive interest in the energy storage domain due to its high theoretical capacity of 946 mA h g−1. However, the inherent disadvantages of serious volume expansion and poor conductivity restrict the development of Sb2S3 for its application in SIBs. In addition, chemical synthesis is a main method to prepare Sb2S3, which is commonly accompanied by environmental pollution and excessive energy consumption. Herein, the natural stibnite mineral was directly applied in SIBs after modification with graphite via an effective and facile approach. The novel composites exhibited excellent electrochemical properties with higher reversible capacity, better rate capability and more outstanding cycling stability than the bare natural stibnite mineral. Briefly, this study is anticipated to provide a reference for the development of natural minerals as first-hand materials in energy storage and a new approach to improve natural stibnite mineral composites for their application as anodes in SIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...