Enhanced cellular uptake and photochemotherapeutic potential of a lipophilic strained Ru(ii) polypyridyl complex†
Abstract
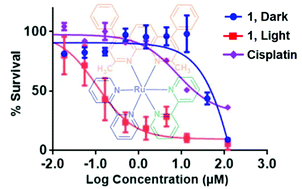
The use of ruthenium complexes as chemotherapeutic agents has been recently explored as one of the alternatives to conventional treatments. In the present study, two Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes were synthesized and characterized: a strained [Ru(bipy)2(BC)]Cl2 (complex 1) where [bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine and BC = bathocuproine] along with the unstrained control [Ru(bipy)2(phen)]Cl2 (complex 2) where [phen = 1,10-phenanthroline]. The photophysical and photochemical analyses proved that unlike the photostable complex 2, complex 1 ejected both bipy and BC ligands at a ratio of 3 : 1 respectively. Results showed that the activity of complex 1 was significantly enhanced upon photoactivation. The response was however particularly significant in B16-F10 melanoma cells where phototoxicity index (PI = IC50 dark/IC50 light) was >900. When compared to cisplatin, the photoproducts were more potent against all tested cell lines, implying that the complex acquired significant chemotherapeutic potential upon irradiation. Cellular uptake of complex 1 and the free BC ligand were found to be significantly facilitated as evidenced by 400–600 fold increase in concentration of the compounds inside the cells relative to the extracellular culture medium. Complex 2 exhibited 35 times lower cellular concentration relative to complex 1. Flow cytometry and plasmid DNA gel electrophoresis measurements showed that complex 1 interacts with DNA inducing apoptosis in the dark and either late-apoptosis or necrosis upon irradiation. These findings corroborate the importance of lipophilic ligands such as BC to enhance uptake and subsequently improve the photochemotherapy potential of Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' Collection: Metals in Medicine


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...