Degradation and biocompatibility of a series of strontium substituted hydroxyapatite coatings on magnesium alloys
Abstract
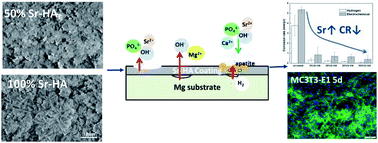
There has been a surge in the research on magnesium (Mg) alloys as a promising selection for biomaterials application. However, as a foremost drawback, the fast degradation of Mg alloys limits its clinical use. In this study, a series of Sr-HA coatings with the Sr content ranging between 10–100% were prepared on Mg alloys, in order to control the degradation and enhance the osteoblast response. Microstructure analysis indicated the formation of Ca10−xSrx(PO4)6(OH)2 coatings with the thickness ranging between 28–35 μm. The degradation results suggested that an increase in the Sr content in the coatings led to the decreasing degradation rate of the Sr-HA coated Mg. 100% Sr-HA coatings provided the best corrosion protective effect with nearly no hydrogen evolution during 10 days' immersion in Hank's solution. The in vitro cell biocompatibility was evaluated with MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts using the extract assay. In each case the released Sr affected the osteoblast proliferation and the expression of osteogenesis markers including, ALP, Col-I and RUNX2, in a Sr concentration-dependent manner. These results suggest that Sr-HA coating is a promising combination for controlling the degradation and enhancing the cytocompatibility of Mg alloys. The degradation and osteoblast response could be simply controlled through the adjustment of Sr content in the coatings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...