Facile synthesis of exfoliated vermiculite nanosheets as a thermal stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride resin
Abstract
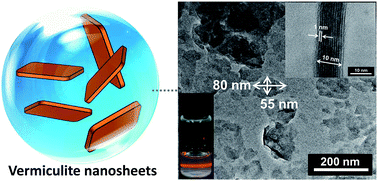
Well-defined vermiculite (VMT) nanosheets have been exfoliated from mineral VMT by a water-assisted anion-exchange approach. The resultant VMT nanosheets are utilized as a thermal stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to resist dehydrochlorination of PVC. As expected, the color-blackening onset of PVC is delayed after incorporating VMT nanosheets, and the thermal stability improves with reducing the particle size of the VMT nanosheets. The dehydrochlorination temperature appears to be increased by 13 °C for the PVC resin with 6 wt% VMT additive. The improved thermal stability is attributed to the negatively charged laminates of VMT that stabilize hydrogen chloride produced from thermal degradation of PVC. This work not only provides a cost-effective approach to prepare VMT nanosheets but also presents new insight towards the design of thermal stabilizers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...