Tannic acid-stabilized gold nano-particles are superior to native tannic acid in inducing ROS-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells via the p53/AKT axis†
Abstract
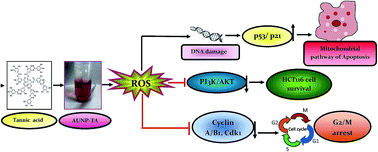
Gold nanoparticle formulated tannic acid (AuNP-TA) was synthesized, and its anticancer activity was compared to that of free tannic acid (TA). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was reduced by half when cell lines were treated with AuNP-TA as compared to IC50 values upon free TA treatment. Both showed better cytotoxic activity in HCT116 cell line as compared to MCF7 and HepG2. AuNP-TA induced death of HCT116 cells was associated with characteristic apoptotic changes. At the same treatment dose, AuNP-TA generated more ROS, caused a more extensive DNA damage and promoted higher expression of p53 and p21 than TA. Treatment with AuNP-TA regulated generation of p53 and ROS bi-directionally. Binding studies showed that TA lowered the expression of Akt, which inhibited the survival of colon cancer cells. Also, cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, enhanced expression of caspase-3/9, Bak, and Bax, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and enhanced level of cytosolic cytochrome c were observed in AuNP-TA treated HCT116 cells. Thus, AuNP-TA is more efficient than TA in inducing apoptotic cell death of HCT116 cells via the ROS/P53/Akt axis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...