Philic–phobic chemical dynamics of a 1st tier dendrimer dispersed o/w nanoemulsion†
Abstract
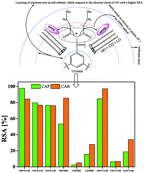
Olive, castor and linseed oil (oil-in-water) nanoemulsions were prepared using Tween-20, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (0.12 w/w%) with 0.02 w/w% cellulose acetate propionate (CAP), 0.02 w/w% cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB), 6.2 w/w% ethyl acetate, 5.5 w/w% ethanol and 7.8 w/w% glycerol as dispersion agents. To study the dispersion effect of trimesoyl 1,3,5-tridimethyl malonate (TTDMM, 1st tier), nanoemulsions were prepared with olive, castor and linseed oil. Their density, viscosity, surface tension and friccohesity measurements at T = (293.15, 303.15, and 315.15) K, hydrodynamic radii, surface excess concentration, surface area per molecule, and antioxidant activities were studied. Dispersion variations of TTDMM on varying surfactant and specific interactions of the hydration spheres and ester moiety of TTDMM with ethyl acetate, ethanol and glycerol linked oil–water–surfactant networks have been established. The variations in physicochemical properties suggest that the oil–TTDMM interaction abilities of the surfactant and co-surfactant moieties in the nanoemulsions cause a hydrophobic segregation. The physicochemical study of both blank and TTDMM loaded nanoemulsions have illustrated the thermodynamic stabilities in terms of hydrophobic–hydrophilic, hydrophilic–hydrophilic, van der Waals and hydrogen bonding interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...