Enzymatic synthesis of selenium-containing amphiphilic aliphatic polycarbonate as an oxidation-responsive drug delivery vehicle†
Abstract
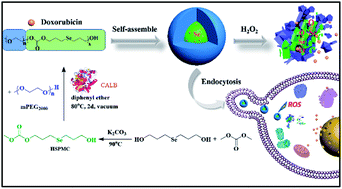
Although functional aliphatic polycarbonates (APCs) have attracted prominent research interest as stimuli-responsive biomaterials, the majority of functional APCs are fabricated by detrimental organometallic catalysts or organo-catalysts. Herein, a facile synthetic strategy based on enzymatic polymerization was developed to construct a selenium-containing amphiphilic aliphatic polycarbonate (mPEG-b-CMP45). Specifically, the selenium in its backbone framework underwent a hydrophobic–hydrophilic transition upon exposure to the abnormal ROS level of the tumor, thus providing a promising platform for ROS-triggered drug release. This amphiphilic mPEG-b-CMP45 efficiently encapsulated doxorubicin (DOX) via self-assembly in aqueous solution and showed an excellent ability to regulate the release of DOX in response to H2O2 at biologically relevant concentrations (100 μM). These DOX-loaded nanoparticles could easily be internalized into U87 cells and possess the inherent antitumor properties of DOX, while they exhibited much lower cytotoxicity in normal cells HL-7702. Moreover, in many cases, the introduction of selenium caused high cytotoxicity of the materials, but the cytotoxicity results in HL-7702 cells demonstrated the good biocompatibility of mPEG-b-CMP45. These collective data suggested the potential use of mPEG-b-CMP45 as a biocompatible and smart drug delivery vehicle.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' Collection: Metals in Medicine


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...