Insight into the effect of quinic acid on biofilm formed by Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
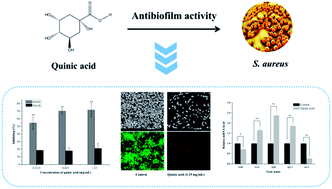
The biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus on food contact surfaces is the main risk of food contamination. In the present study, we firstly investigated the inhibitory effect of quinic acid (QA) on biofilm formed by S. aureus. Crystal violet staining assay and microscopy analysis clearly showed that QA at sub-MIC concentrations was able to significantly reduce the biofilm biomass and cause a collapse on biofilm architecture. Meanwhile, fibrinogen binding assay showed that QA had obviously effect on the S. aureus bacteria adhesion. XTT reduction assay and confocal laser scanning microscopic images revealed that QA significantly decreased metabolic activity and viability of biofilm cells. In addition, qRT-PCR analysis explored the potential inhibitory mechanism of QA against biofilm formation, which indicated that QA significantly repressed the gene sarA and activated the gene agrA. Moreover, QA exhibited a highly ability to reduce the number of sessile S. aureus cells adhered on the stainless steel. So, it was suggested that QA could be used as a promising antibiofilm agent to control biofilm formation of S. aureus.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' collection: Chemical Biology


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...