In vitro evaluation of anti-hepatoma activity of brevilin A: involvement of Stat3/Snail and Wnt/β-catenin pathways
Abstract
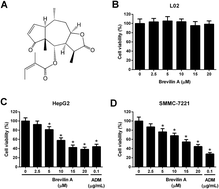
Brevilin A, a natural sesquiterpene lactone extracted from Centipeda minima, has been found to exhibit anti-tumor effect. However, the roles of brevilin A on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not yet been reported. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of brevilin A in HCC and the underlying in vitro mechanisms. The HCC cell lines, HepG2 and SMMC-7221, were treated with different concentrations of brevilin A (0 μM, 2.5 μM, 5 μM, 10 μM, 15 μM, and 20 μM) for 48 h. MTT assay was performed to detect the cell viability. Flow cytometry was performed to detect cell apoptosis. Cell invasion was detected using the transwell assay. The expressions of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-Stat3), Stat3, Snail, β-catenin, and c-Myc were detected using the western blot analysis. The results showed that brevilin A reduced cell viability and invasion in HepG2 and SMMC-7221 cells. The apoptotic rates of HepG2 and SMMC-7221 cells treated with brevilin A were found to be markedly increased. The expression levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were decreased after the treatment with brevilin A. In addition, brevilin A suppressed the Stat3/Snail and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in HCC cells. Collectively, brevilin A displayed an anti-tumor effect against HCC in vitro, which might be attributed to the inactivation of Stat3/Snail and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' collection: Chemical Biology


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...