Interaction landscape of a ‘CαNN’ motif with arsenate and arsenite: a potential peptide-based scavenger of arsenic†
Abstract
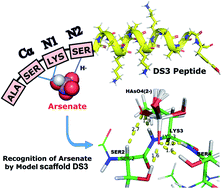
Arsenic (As) is a toxic metalloid that has drawn immense attention from the scientific community recently due to its fatal effects through its unwanted occurrence in ground water around the globe. The presence of an excess amount of water soluble arsenate and/or arsenite salt (permissible limit 10 μg L−1 as recommended by the WHO) in water has been correlated with several human diseases. Although arsenate (HAsO42−) is a molecular analogue of phosphate (HPO42−), phosphate is indispensable for life, while arsenic and its salts are toxic. Therefore, it is worthwhile to focus on the removal of arsenic from water. Towards this end, the design of peptide-based scaffolds for the recognition of arsenate and arsenite would add a new dimension. Utilizing the stereochemical similarity between arsenate (HAsO42−) and phosphate (HPO42−), we successfully investigated the recognition of arsenate and arsenite with a naturally occurring novel phosphate binding ‘CαNN’ motif and its related designed analogues. Using computational as well as biophysical approaches, for the first time, we report here that a designed peptide-based scaffold based on the ‘CαNN’ motif can recognize anions of arsenic in a thermodynamically favorable manner in a context-free system. This peptide-based arsenic binding agent has the potential for future development as a scavenger of arsenic anions to obtain arsenic free water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...