Revealing an unusual temperature-dependent CO2 adsorption trend and selective CO2 uptake over water vapors in a polyamine-appended metal–organic framework†
Abstract
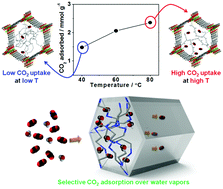
We report the development of a tetraethylenepentamine (tepa)-functionalized Mg2(dobpdc) (T02, T2, T20, and T200; the number denotes equivalents of tepa used with respect to the framework), which uncommonly exhibited a gradual increase in CO2 uptake with increasing temperature when polyamine groups were heavily loaded into the framework (T20 and T200). For the moderately loaded sample (T2), a significant working capacity (11.2 wt%) and a cyclable CO2 performance at 40 °C and 15% CO2 pressure were obtained. The abrupt increase observed in the CO2 isotherms indicates that the tepa-loaded samples involve a CO2 insertion mechanism. Interestingly, all amine groups in tepa can partly participate in the formation of ammonium carbamate ion pairs, which is the first observation of this in amine-functionalized metal–organic frameworks. Remarkably, we demonstrate that high loading of tepa allowed for selective CO2 uptake over H2O vapors, together with enhanced framework stability under humid conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...