Functionalized 2-hydrazinobenzothiazole with carbohydrates as a corrosion inhibitor: electrochemical, XPS, DFT and Monte Carlo simulation studies
Abstract
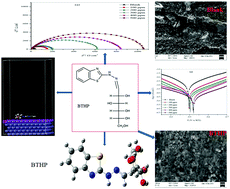
In the present investigation two hydrazinobenzothiazole compounds 6-(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)hydrazono)hexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol (BTHP) and 5-(2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)hydrazono)pentane-1,2,3,4-tetraol (BTHT) were prepared. These compounds having heteroatoms as active sites were investigated for scaling down the corrosion process in N80 steel. The effectiveness of these inhibitors was monitored by gravimetric and electrochemical methods. Observations suggested that the mechanism of inhibition is mainly due to the adsorption of these inhibitors on the metal surface, and adsorption follows the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Tafel polarization curves show that these are mixed type inhibitors. Morphological studies were done by FESEM and the composition of the protective layer at the surface of the sample was analyzed using an XPS instrument. FESEM images indicate the formation of a protective layer on the metal surface which slows down the process of corrosion. DFT and Monte Carlo simulations provide the valuable quantum parameters of the studied compounds which are supportive of the results obtained from gravimetric and electrochemical methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...