Direct visualization of the ouzo zone through aggregation-induced dye emission for the synthesis of highly monodispersed polymeric nanoparticles†
Abstract
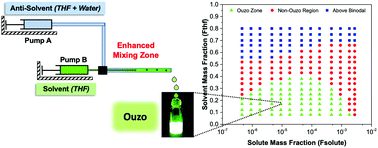
Polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) have drawn significant attention for use in optoelectronic devices and biomedical applications. Among their physiochemical properties, the size of NPs is considered to be one of their most crucial parameters. Taking the encapsulation of hydrophobic drug or dye molecules into biocompatible polymers as an example, the solvent displacement method (also known as nanoprecipitation) offers good control over the mixing process to synthesize NPs with sizes ranging from 25 to 300 nm. However, nanoprecipitation produces large aggregates above a certain solvent fraction and polymer concentration, which results in the synthesis of highly polydisperse particles with uncontrolled sizes. Therefore, for the systematic and controlled synthesis of monodispersed NPs, we have plotted the ouzo zones of two polymers, PLGA and DSPE–mPEG, in a novel and simple way by taking advantage of the unique properties of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) dyes, which show different fluorescence emissions in different states. Furthermore, we have developed a new process, the enhanced solvent displacement method (ESDM), for the production of highly monodispersed NPs with ultra-low PDI values (0.05 to 0.1) and sizes ranging from 25 to 200 nm by increasing the miscibility between the anti-solvent and solvent with pre-mixing of the solvent (tetrahydrofuran) into the anti-solvent (water).
- This article is part of the themed collections: Introducing the Reaction Chemistry & Engineering Associate Editors and Recent Progress on Aggregation-Induced Emission


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...