A review of the advanced developments of electrochemical sensors for the detection of toxic and bioactive molecules
Abstract
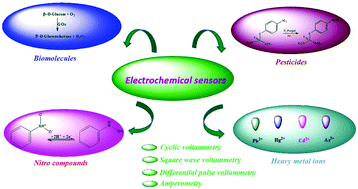
Herein, the design and development of novel sensitive and cost-effective electrochemical sensors based on various classes of nanocomposites fabricated by different methods for the detection of biomolecules (glucose, dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid), heavy metal ions (Pb2+, Hg2+, Cd2+ and As3+) and environmental pollutants (hydrazine, nitrobenzene, nitrophenols and pesticides) are reviewed. Furthermore, the recent developments of electrochemical sensors, biosensors and pesticide sensors constructed using different nanocomposite materials having different morphologies for the reactive monitoring of food additives, human health and environmental safety are reviewed and presented. Interestingly, electrochemical techniques have received significant attention due to their remarkable durability; moreover, potential candidates for implementation in the real-time detection of analytes can be found in the recently reported studies. Advanced state-of-the-art nanostructured materials, such as nanorods, nanocubes, nanoneedles, nanoflowers, nanotubes and nanobundles, have the potential for application in electrochemical sensing platforms as they demonstrate high-performance electrochemical sensitivity, selectivity and long-term stability.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...