Thermal stability of aluminum oxide nanoparticles: role of oxygen concentration†
Abstract
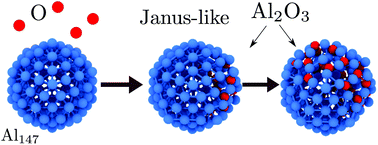
Oxygen absorption and the thermal stability of Al147 nanoparticles were studied by means of classical molecular dynamics simulations and Monte Carlo methods. The results suggest that for the studied sizes, oxygen incorporation yields an Al2O3 nanoparticle with a Janus-like morphology, contrary to the expected core–shell nanostructure observed in simulations and experiments of nanometer-size nanoparticles. A simulated annealing, introduced to support this assumption, shows that the Janus-like morphology has a lower energy than that of Al@Al2O3 with a core@shell conformation. Also, the thermal behavior of a Janus-like Al/Al2O3 nanoparticle as a function of oxygen concentration was investigated. It is observed that the partial oxidation reduces the nanoparticle melting temperature because the number of pure aluminum atoms is reduced. In fact, the melting point can be as low as 400 K for an Al147O30 nanoparticle. The melting process leads to a solid alumina region that coexists with liquid-like aluminum nanoparticles. The oxide never adopts a protective shell covering configuration of the aluminum nanoparticle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...