Controlling the supramolecular polymerization and metallogel formation of Pt(ii) complexes via delicate tuning of non-covalent interactions†
Abstract
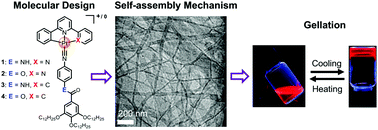
Two ionic and two neutral luminescent platinum(II) isocyanide complexes bearing different linkers (amide vs. ester) 1–4 have been rationally designed and synthesized. Their supramolecular polymerization and gelation properties have been comprehensively investigated by spectroscopic studies. Significant emission enhancement was observed upon aggregation, with their emission maxima highly dependent on pincer ligands. Due to the additional ionic interaction, two ionic complexes 1–2 provide stronger driving forces for the supramolecular polymerization than the neutral derivatives 3–4. Moreover, different linkers (amide vs. ester) were found to lead to distinct supramolecular polymerization mechanisms. Amide-bearing complex 1 undergoes highly cooperative supramolecular polymerization, while replacement of the amide by ester groups leads to isodesmic self-assembly. Unexpectedly, only ester-containing derivative 2 can form reversible metallogel. The reason is attributed to its synergistic participation of π–π and ionic interactions, as well as suitable organization of anions. This work presented here highlights that subtle variation of noncovalent interactions, particularly hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions, exerts pronounced influence on the supramolecular self-assembly mechanism and gel formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...