Triazine-functionalized covalent benzoxazine framework for direct synthesis of N-doped microporous carbon†
Abstract
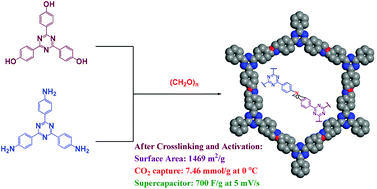
A covalent benzoxazine framework (CBF) was synthesized through a one-pot Mannich reaction of the planar molecules 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)triazine (TAPT) and 2,4,6-tris(p-hydroxyphenyl)triazine (THPT) with paraformaldehyde. This covalent benzoxazine framework underwent thermal curing to generate a highly cross-linked covalent benzoxazine framework (CCBF), with subsequent carbonization and KOH activation providing a nitrogen-doped microporous carbon (N-DMC)—prepared without the need for a template. This nitrogen-doped microporous carbon possessed a spherical morphology, excellent thermal stability (with a Td5 value of 663 °C and a char yield of 85%), a high BET surface area (1469 m2 g−1), and a pore size of 2.07 nm. The thermal transformations from the CBF to the CCBF and then to N-DMC enhanced the CO2 capture ability and electrochemical capacitance. The nitrogen-doped microporous carbon displayed excellent CO2 capture capacities of 3.85 and 7.46 mmol g−1 at 298 and 273 K, respectively; moreover, it provided an electrochemical capacitance of 185 F g−1 at a current density of 1.0 A g−1, as well as excellent stability (average capacitance retention of 87% at 20 A g−1 after 4000 cycles).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...