Reactive oxygen species-responsive nanoparticles based on a thioketal-containing poly(β-amino ester) for combining photothermal/photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy†
Abstract
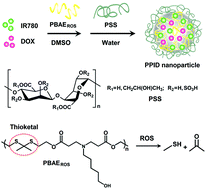
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive nanocarriers have shown great potential for cancer treatment due to the elevated levels of ROS in cancer cells. In this study, we synthesized a novel ROS-responsive poly(β-amino ester) (PBAEROS) through introduction of thioketal groups in its monomer structure and used it as a carrier material to prepare nanoparticles for the co-loading and controlled release of a near-infrared photosensitizer IR780 and a chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin (DOX), thus hoping to obtain synergistic anticancer effects by combining photothermal/photodynamic therapy (PTT/PDT) and chemotherapy. IR780 and DOX co-loaded PBAEROS nanoparticles surface modified with a marine sulfated polysaccharide, named PPID nanoparticles, were prepared using a simple nanoprecipitation method. PPID nanoparticles had a core–shell structure, spherical morphology and uniform size below 200 nm. PPID nanoparticles displayed a significant response ability for ROS and released DOX in a controlled manner. Upon 808 nm laser irradiation, PPID nanoparticles triggered a rapid temperature elevation and induced the generation of a large amount of cytotoxic ROS simultaneously, demonstrating their high PTT/PDT efficiencies. In hepatoma cells, PPID nanoparticles improved the cellular internalization of IR780 and DOX and furthermore notably inhibited the cell proliferation after laser irradiation, indicating the synergistic anticancer effects of PTT/PDT and chemotherapy. Thus it can be seen that we provide a promising ROS-responsive nanocarrier for cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...