Kinetics and mechanism for thermal and photochemical decomposition of 4,4′-azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid) in aqueous media†
Abstract
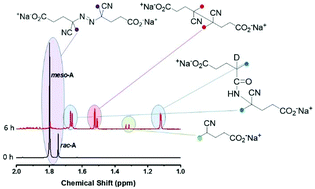
4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid) comprises two diastereoisomers that decompose at different rates in aqueous media [racemic-ACPA: Ea = 132.2 kJ mol−1, A = 4.76 × 1015 s−1, 10 h t1/2 = 65 °C; meso-ACPA: Ea = 131.7 kJ mol−1, A = 2.98 × 1015 s−1,10 h t1/2 = 67 °C], but both decompose at a similar though faster rate in N,N-dimethylformamide [Ea = 134.0 kJ mol−1, A = 1.26 × 1016 s−1,10 h t1/2 = 63 °C]. The major product of decomposition in both aqueous and organic media is the ketenimine formed by C–N coupling of the radicals formed, which is irreversibly trapped as an amide in aqueous media.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...