Self-healing and shape-memory properties of polymeric materials cross-linked by hydrogen bonding and metal–ligand interactions†
Abstract
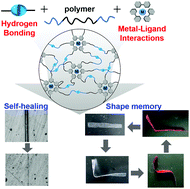
Polymeric materials were prepared by cross-linking them with two independent non-covalent interactions, namely hydrogen bonding and metal–ligand interactions. The fracture energy of the resultant polymeric material is higher than that of the polymeric material without non-covalent interactions as well as that with one non-covalent interaction. Moreover, the prepared polymeric materials show self-healing and shape memory properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...