Thioalkyl- and sulfone-substituted poly(p-phenylene vinylene)s†
Abstract
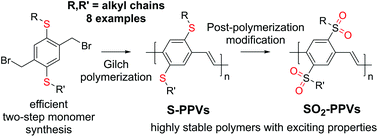
Poly(p-phenylene vinylene)s (PPVs) have been studied for decades, but research on this interesting class of conjugated polymers is far from being completed. New applications like in bioimaging keep emerging and even simple structural variations are still waiting to be explored. Surprisingly, not even dithioalkyl-substituted PPVs (S-PPVs) have been reported in the peer-reviewed literature, although the corresponding dialkoxy-substituted PPVs (O-PPVs) like MEH-PPV or MDMO-PPV are most frequently used and although thioalkyl substituents can improve the material properties significantly. We herein report the development of a highly efficient, scalable two-step synthesis of Gilch monomers for S-PPVs starting from low-cost 1,4-diiodobenzene. A low-temperature polymerization protocol has been developed for these monomers, affording high-molecular weight S-PPVs in excellent yields. The thermal, electrochemical, and photophysical properties of S-PPVs are reported to highlight the potential of these polymers. Furthermore, treatment with dimethyldioxirane is demonstrated to result in rapid conversion into sulfone-substituted PPVs (SO2-PPVs), introducing a route to high-molecular weight SO2-PPVs with exceptional stability and solid-state photoluminescence quantum yields of up to 0.46.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...