Multi-stimuli responsive poly(amidoamine) dendrimers with peripheral N-dialkylaminoethyl carbamate moieties†
Abstract
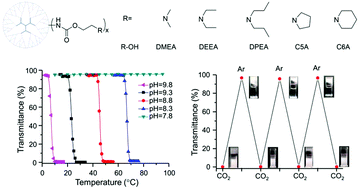
A novel type of multi-stimuli responsive dendrimer with thermo-, pH-, and CO2-responsiveness was developed through facile modification of polyamidoamine dendrimers (PAMAM) with various N-dialkylaminoethyl carbamate moieties. A series of modified PAMAM dendrimers with a well controlled structure were obtained and characterized by 1H NMR. The aqueous solutions of these dendrimers showed a lower critical solution temperature (LCST)-type thermoresponse, and their cloud point temperature (Tcp) was determined by turbidity measurements. Tcp was tunable from 8 to 70 °C, depending on the hydrophobicity and substitution number of the terminal N-dialkylaminoethyl groups, PAMAM generation, pH values, and salt concentrations. Additionally, the solubility of the resultant dendrimers could be reversibly modulated by alternately bubbling CO2 and argon. Our study offers a simple but effective approach to making new multi-stimuli responsive dendrimers for potential smart material applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...