Optimizing the Cu-RDRP of N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide toward biomedical applications†
Abstract
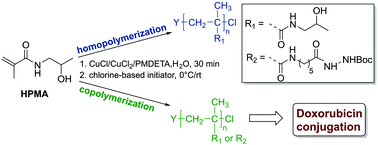
Aqueous Cu-RDRP of N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide, a monomer with important biomedical applications, was optimized with respect to monomer conversion (82–99%), product dispersity (<1.25), and molecular weight control (up to 100 000). For this purpose, different chlorine-based initiators in conjunction with the CuCl/CuCl2/PMDETA catalytic system were used. The utility of the optimized method in the biomedical field was demonstrated in the preparation of the poly(HPMA)-based copolymeric carrier having the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin conjugated through a pH-sensitive hydrazone linker.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...