An alternative approach to create N-substituted cyclic dipeptides†
Abstract
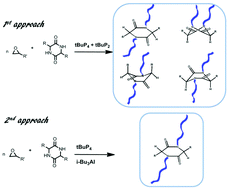
N-Modified peptide backbones are promising peptidomimetics which offer several advantages in terms of improved biological activity and stability. They further allow the development of novel functional materials. However, the synthesis of N-substituted peptides is very challenging with the existing methods, particularly the synthesis of peptides with larger N-substituents. In this work, we are introducing a new method to create N-polyether substituted cyclic dipeptides via anionic ring-opening polymerization (AROP). Four different cyclic dipeptides with different hydrophobic functional groups were selected to create N-substituted cyclic dipeptides. Backbone amides –NH– were deprotonated with phosphazene bases to form nucleophilic initiators. Furthermore, the effect of different phosphazene bases (tBuP4 and tBuP2) and of the addition of a Lewis acid (i-Bu3Al) was studied in detail towards creating N-polyether-cyclic dipeptides bearing either hydrophobic poly(butylene oxide) chains, or hydrophilic linear polyglycidol chains, thanks to the polymerization of 1,2-epoxybutane and the polymerization followed by the deprotection of t-butyl glycidyl ether monomers, respectively. Moreover, we have demonstrated the possibility of avoiding the isomerization of cyclic dipeptides during the synthesis of N-substituted analogues depending on the synthetic approach.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...