Strategies from nature: polycaprolactone-based mimetic antimicrobial peptide block copolymers with low cytotoxicity and excellent antibacterial efficiency†
Abstract
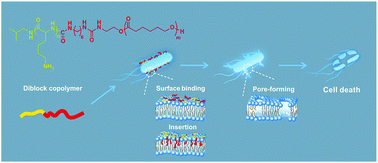
The resistance of bacteria to antibiotics has caused serious threats to public health and it is urgent to develop novel antibacterial agents that do not induce drug resistance. Herein, a series of novel antibacterial copolymers, PCL16-b-Kn, mimicking the structure and action mechanism of natural antimicrobial peptides is reported. The diblock copolymers were synthesized via ring-opening polymerization and facile coupling reaction. The antibacterial results confirmed that the diblock copolymers possess superior antibacterial activities and exhibit rapid bactericidal action against both S. aureus and E. coli. A conclusion can be drawn that the antibacterial activity can be promoted by achieving a balance between the cationic and hydrophobic segments in the copolymers. Further hemolysis and cytotoxicity tests suggest the excellent biocompatibility of these diblock copolymers. Overall, our synthetic strategy demonstrates a new concept of designing novel biocompatible antibacterial copolymers and expands the categories of next-generation antibacterial agents without inducing drug resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...