Association between solar ultraviolet doses and vitamin D clinical routine data in European mid-latitude population between 2006 and 2018†
Abstract
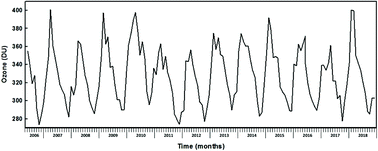
The major source of vitamin D in humans is the ultraviolet radiation-dependent cutaneous synthesis of cholecalciferol; however, low vitamin D status is common in Europe even at mid-latitudes. The UV-radiation that reached the Earth's surface near Milan between May 2006 and December 2018 was retrieved from the TEMIS database and matched with the serum vitamin D levels measured in 30 400 people living in the same area. The results showed a high percentage of insufficient vitamin D levels (measured as 25-hydroxy-vitamin D) throughout the years. During the “vitamin D winter” (November–March) up to 60–90% of the population shows deficient/insufficient (<20–30 ng mL−1) levels of vitamin D and it is explained by the difficulty in obtaining the recommended UV vitamin D doses. In contrast, the warm season provides plenty of UV-radiation, but still 30–50% of the population shows deficient/insufficient vitamin D levels. The circannual vitamin D variations were less evident in the female groups which, in the cold season, show values higher than the corresponding male groups. An age group analysis explained this difference by the strongly recommended vitamin D intake for post-menopausal women. In conclusion, increasing the medical advice for vitamin D intake is strongly recommended to improve the vitamin D status at European mid-latitudes. Our findings suggest that UV availability alone cannot explain the vitamin D status of the population which instead is likely to be influenced by several other factors related to both the people's lifestyle and their personal characteristics. A desirable vitamin D range considering the time of the year and sun exposure, but also including factors not related to UV-radiation, would probably result in a more accurate diagnosis of the patients’ vitamin D status. Despite the relatively large time interval, no evident effects due to climate changes were observed in the vitamin D levels during the almost 13 years of analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...