Energy transfer-mediated white light emission from Nile red-doped 9,10-diphenylanthracene nanoaggregates upon excitation with near UV light†
Abstract
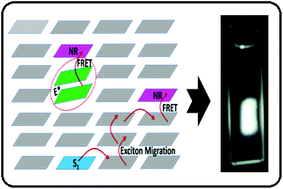
The low cost, ease of preparation, colour tunability and wide application range garnered huge research interest on organic light emitting diode materials (OLED). The development of white light-emitting organic diode materials is mostly targeted for this. Anthracene derivatives have recently emerged as low-cost and efficient blue light-emitting diodes. However, developing efficient organic diode materials that cover the entire visible spectrum is very challenging. Herein, we demonstrated that Nile red (NR)-doped 9,10-diphenylanthracene (DPA) nanoaggregates provided strong white light emission upon excitation with near UV light. The dual emissions of the DPA nanoaggregates covering the blue and green regions were exploited and combined with the controlled red emission of the properly doped NR dye to cover the full visible spectrum, rendering white light emission with a quantum yield of >0.4. The fluorescence spectra of the DPA nanoaggregates doped with NR at various concentrations were monitored and their CIE coordinates were followed to evaluate the proper doping ratio for equal-energy white-light emission. Concurrent time-resolved emission studies provided mechanistic insights into the energy transfer from the exciton and excimer states of DPA to NR. It was revealed that the energy transfer from the singlet excitonic state of DPA followed the diffusion-assisted resonance energy transfer (RET) model. On the other hand, the excimer state showed negligible diffusion and energy transfer from this state found to follow the single-step Förster resonance energy transfer mechanism. The observation of efficient white light emission in the doped DPA nanoaggregates was proposed to have prospective applications in OLED devices, given the fact that triplet excitons may be exploited for emission through the efficient triplet–triplet annihilation contribution to fluorescence enhancement.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...