Neutral iridium(iii) complexes bearing BODIPY-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands: synthesis, photophysics, in vitro theranostic photodynamic therapy, and antimicrobial activity†
Abstract
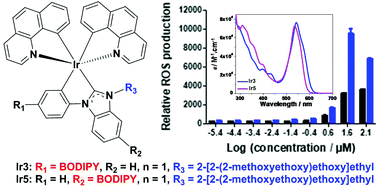
The synthesis, photophysics, and photobiological activities of a series of novel neutral heteroleptic cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes incorporating boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) substituted N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands (Ir1–Ir5) are reported. The effect of the substitution position of BODIPY on the NHC ligands, either on C4 of the phenyl ring (Ir1–Ir3) or C5 of the benzimidazole unit (Ir4 and Ir5), and its linker type (single or triple bond) on the photophysical properties was studied. Ir1–Ir5 exhibited BODIPY-localized intense 1IL (intraligand transition)/1MLCT (metal-to-ligand charge transfer) absorption at 530–543 nm and 1,3IL/1,3CT (charge transfer) emission at 582–610 nm. The nanosecond transient absorption results revealed that the lowest triplet excited states of these complexes were the BODIPY-localized 3π,π* states. Complexes Ir4 and Ir5 exhibited blue-shifted 1IL absorption and 1,3IL/1,3CT emission bands compared to the corresponding absorption and emission bands in complexes Ir1 and Ir3. However, replacing the methyl substituents on N3 of benzimidazole in complexes Ir1 and Ir4 with oligoether substituents in Ir3 and Ir5, respectively, did not impact the energies of the low-energy absorption and emission bands in the corresponding complexes. Water-soluble complexes Ir3 and Ir5 have been explored as photosensitizers for in vitro photodynamic therapy (PDT) effects toward human SKMEL28 melanoma cells. Ir3 showed no dark cytotoxicity (EC50 > 300 μM) but good photocytotoxic activity (9.66 ± 0.28 μM), whereas Ir5 exhibited a higher dark cytotoxicity (20.2 ± 1.26 μM) and excellent photocytotoxicity (0.15 ± 0.01 μM). The phototherapeutic indices with visible light (400–700 nm) activation were >31 for Ir3 and 135 for Ir5. Ir3 and Ir5 displayed 1O2 quantum yields of 38% and 22% in CH3CN, respectively, upon 450 nm excitation. Ir5 was more effective at generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) in vitro. Ir5 was also active against Staphylococcus aureus upon visible light activation, with a phototherapeutic index of >15 and EC50 value of 6.67 μM. These photobiological activities demonstrated that these neutral Ir(III) complexes are promising in vitro PDT reagents, and substitution at C5 on the benzimidazole group of the NHC ligand was superior to C4 substitution on the phenyl ring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
