Double C–N bond cleavages of N-alkyl 4-oxopiperidinium salts: access to unsymmetrical tertiary sulfonamides†
Abstract
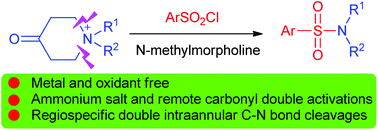
In this paper, regiospecific, double intraannular C–N bond cleavages of N-alkyl 4-oxopiperidinium salts are presented. The reaction sequence involves a charge-transfer complex, in situ formed between sulfonyl chloride and N-methylmorpholine, which induces S–Cl bond homolysis of sulfonyl chloride, yielding a reactive sulfonyl radical that further induces the double C–N bond cleavages of N-alkyl 4-oxopiperidinium salt. The secondary amine thus produced was trapped by sulfonyl chloride to yield the desired sulfonamide product. The key feature of this protocol is that two intraannular C–N bonds of the 4-oxopiperidine ring are cleaved in one step under metal- and oxidant-free conditions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...