Clickable styryl dyes for fluorescence labeling of pyrrolidinyl PNA probes for the detection of base mutations in DNA†
Abstract
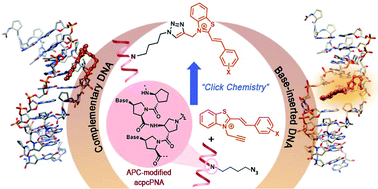
Fluorescent hybridization probes are important tools for rapid, specific and sensitive analysis of genetic mutations. In this work, we synthesized novel alkyne-modified styryl dyes for conjugation with pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acid (acpcPNA) by click chemistry for the development of hybridization responsive fluorescent PNA probes. The free styryl dyes generally exhibited weak fluorescence in aqueous media, and the fluorescence was significantly enhanced (up to 125-fold) upon binding with DNA duplexes. Selected styryl dyes that showed good responses with DNA were conjugated with PNA via sequential reductive alkylation-click chemistry. Although these probes showed little fluorescence change when hybridized to complementary DNA, significant fluorescence enhancements were observed in the presence of structural defects including mismatched, abasic and base-inserted DNA targets. The largest increase in fluorescence quantum yield (up to 14.5-fold) was achieved with DNA carrying base insertion. Although a number of probes were designed to give fluorescence response to complementary DNA targets, probes that are responsive to mutations such as single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), base insertion/deletion and abasic site are less common. Therefore, styryl-dye-labeled acpcPNA is a unique probe that is responsive to structural defects in the duplexes that may be further applied for diagnostic purposes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...