Cleavage of lignin model compounds and ligninox using aqueous oxalic acid†
Abstract
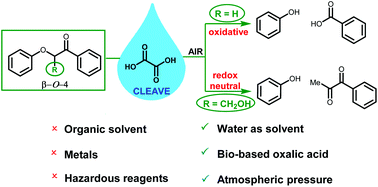
Aqueous oxalic acid cleaves oxidised β-O-4 lignin model compounds by two distinct mechanisms that are dependent on the presence of the hydroxymethyl substituent. Various β-O-4 phenoxyacetophenones that do not contain the hydroxymethyl substituent undergo oxidative cleavage upon exposure to aqueous oxalic acid in the presence of air, likely through concerted ring opening of a dioxetane intermediate to give the corresponding benzoic acid and phenyl formate. Importantly, detrimental side reactions arising from singlet oxygen and hydroperoxy radicals (from both O2 and oxalic acid) are minimal when the cleavage is run under air compared to neat oxygen. When oxidised β-O-4 lignin model compounds bearing the hydroxymethyl group are cleaved by aqueous oxalic acid, the resulting diketone and phenol products arise from a redox neutral cleavage that is analogous to the formic acid-sodium formate mediated lignin cleavage process reported by Stahl. Aqueous oxalic acid also cleaves lignin itself, with oxidised milled wood lignin (MWLox) from Pinus radiata giving a 14% yield of ethyl acetate soluble aromatics with good selectivity for vanillin. Aqueous oxalic acid appears to be a promising lignin cleavage system given the benign, bio-based reagents, absence of metals and organic solvents and a simple extraction procedure that enables oxalic acid recycling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...