Binding orientation and reactivity of alkyl α,ω-dibromides in water-soluble cavitands†
Abstract
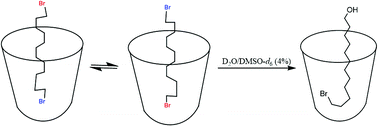
Host–guest complexation of long chain α,ω-dibromides was evaluated in deep water-soluble cavitands 1 and 2. The bound dibromides (C7–C12) tumble rapidly on the NMR timescale and averaged signals were observed. The complexation allows mono hydrolysis of dibromides in aqueous solution. The arrangement of the products in the host–guest complex was fixed in an unsymmetrical manner that protects the guest from further reaction. Up to 93% yields of the mono-alcohols were obtained. The α,ω-dibromides formed a capsule with cavitand 2 and remained unreactive to hydrolysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...