Selective binding of nucleosides to gapped DNA duplex revealed by orientation and distance dependence of FRET†
Abstract
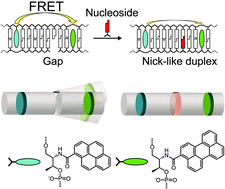
Herein we used orientation and distance dependence of Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) to analyze the binding of nucleosides to a gapped DNA duplex. Binding isotherms and information on the structures of the complexes were obtained by monitoring FRET between pyrene and perylene, which were introduced into the DNA through D-threoninol. FRET efficiency significantly changed upon formation of a duplex with a 1-nucleotide gap and a nucleoside. The FRET plot indicated that the complex has a double helical structure similar to a nicked duplex. Cooperative binding of two nucleosides to a duplex with a 2-nucleotide gap was also revealed using FRET. Various drug-nucleic acids interactions could be investigated using this sensitive and facile method.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...