Mechanistic investigation of superelectrophilic activation of 1,1′-bi-2-naphthols in the presence of aluminum halides†
Abstract
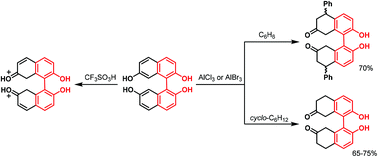
7,7′-Dihydroxy-1,1′-bi-2-naphthol, as a result of superelectrophilic activation in the presence of an excess of aluminum halides, reacts with cyclohexane and benzene to yield 5,6,7,8,5′,6′,7′,8′-octahydro-7,7′-dioxo-bi-2-naphthol and its 5,5′-diphenyl derivative, respectively. In contrast, isomeric 6,6′-dihydroxy-1,1′-bi-2-naphthol does not react at all under the same reaction conditions, while the parent 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol (BINOL) reveals an alternative mode of behavior. The mechanistic aspects of these intriguing results are discussed on the basis of experimental and theoretical (DFT) study of the protonation and complexation properties of the starting BINOLs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanistic, computational & physical organic chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...