Thermal conductivity of V2O5 nanowires and their contact thermal conductance
Abstract
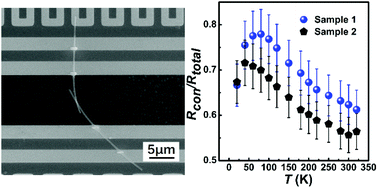
Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5)-based composites show outstanding performances as cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries. However, their inferior thermal conductivity restricts the heat dissipation through the cathode electrode. In this study, we measured the thermal conductivity of V2O5 nanowires using the thermal bridge method and found that their thermal conductivity is 3.84 ± 0.38 W m−1 K−1 at T = 300 K. The contact thermal resistance between two nanowires with the same size was measured to be up to 50%–80% of the total thermal resistance in the measured samples, indicating that their contact is the bottleneck for thermal dissipation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...