Self-templated synthesis of Co3O4 hierarchical nanosheets from a metal–organic framework for efficient visible-light photocatalytic CO2 reduction†
Abstract
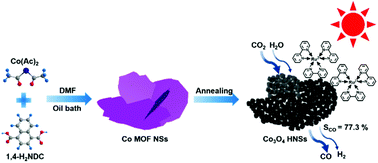
Efficient photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into energy-rich chemicals is of great significance for both environmental conservation and alleviating the energy crisis. However, convenient synthesis of low-cost, durable and eco-friendly photocatalysts with a novel morphology or structure for highly selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction remains a challenge. Herein, Co3O4 hierarchical nanosheets were synthesized by calcination of novel cobalt metal–organic framework (MOF) nanosheets prepared by a facile oil bath method. In such Co MOF nanosheets, 1,4-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid was chosen as the organic linker, rather than the commonly used 2-methylimidazole for ZIF-67. After thermal treatment in air, the obtained Co3O4 inherited the 2D morphology of its MOF template and evolved into hierarchical nanosheets which were composed of small nanoparticles. Benefiting from the large surface area, abundant mesoporous structure and good capability towards the separation and transfer of photo-generated charge carriers induced by less internal oxygen vacancies, the Co3O4 hierarchical nanosheets showed a CO generation rate of 39.70 μmol h−1 in visible-light photocatalytic CO2 reduction, which was superior to that of Co3O4 nanoparticles and commercial Co3O4. What's more, a CO selectivity of 77.3% was achieved, which is among the highest of cobalt-based spinel oxide photocatalysts for CO2 conversion.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editor’s Choice: Functional MOFs and COFs

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...